EPPO Standards
General background
 As a result of the work undertaken by the different technical bodies of the Organization (e.g. Panels and Working Parties), EPPO prepares Standards covering its two main fields of activities (plant protection products and phytosanitary measures). EPPO Standards are recommendations that are addressed to the NPPOs of EPPO member countries. EPPO Standards are also ‘Regional Standards’ in the sense given by the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
As a result of the work undertaken by the different technical bodies of the Organization (e.g. Panels and Working Parties), EPPO prepares Standards covering its two main fields of activities (plant protection products and phytosanitary measures). EPPO Standards are recommendations that are addressed to the NPPOs of EPPO member countries. EPPO Standards are also ‘Regional Standards’ in the sense given by the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
In order to ensure international acceptance, draft standards go through an approval procedure, during which all EPPO member countries have the opportunity to express their views. Final decisions are obtained by consensus and EPPO Standards are officially adopted by the EPPO Council. Following approval, EPPO Standards are published in the EPPO Bulletin and can also be retrieved via this website (via links to the EPPO Bulletin website). In addition, they are stored as PDF documents in the EPPO Global Database. All EPPO Standards except PP1 Standards can be obtained free of charge. PP1 Standards are stored in a dedicated database and registration is required to access specific PP1 standards.
How do I know that new /revised EPPO Standards are available? Subscribe to the ‘Standards’ mailing list
How and where can I find the latest version of an EPPO Standard?
List of EPPO Standards
EPPO Standards have been separated into two main series: PM Standards on phytosanitary measures (covering regulatory measures, treatments, PRA, diagnostics, certification, and safe use of biological control) and PP Standards on plant protection products
EPPO Standards on phytosanitary measures
- PM 1 – General Phytosanitary Measures: recommendations on the use of phytosanitary certificates, the EPPO A1 and A2 Lists of pests recommended for regulation as quarantine pests, and standards on Arthurdendyus triangulatus.
- PM 2 – Pest-specific Phytosanitary Measures: all Standards in this series (previously called SQRs, Specific Quarantine Requirements) are now withdrawn.
- PM 3 – Phytosanitary Procedures: methods to be followed for performing inspections, tests or treatments of commodities moving in trade, or surveys of quarantine pests.
- PM 4 – Production of Healthy Plants for Planting: steps to be followed for the production of vegetatively propagated planting material whose health status is attested by an official certificate (ornamentals, fruit crops, and potatoes).
- PM 5 – Pest Risk Analysis: detailed guidance on the analysis of risk presented by certain pests, in relation to their potential status as quarantine pests or regulated non-quarantine pests.
- PM 6 – Safe use of Biological Control: guidelines for assessing and reducing the risks associated with various aspects of the introduction and use of biological control agents and, as appropriate, for comparing them with the benefits in terms of efficacy.
- PM 7 – Diagnostics: internationally agreed diagnostic protocols for regulated pests and horizontal standards on diagnostic issues.
- PM 8 – Commodity-specific Phytosanitary Measures: recommendations about phytosanitary measures which should be used or required by EPPO member countries for certain commodities moving in trade to prevent introduction and spread of quarantine pests.
- PM 9 – National Regulatory Control Systems: procedures to be followed for official control with the aim of containing and eradicating pests.
- PM 10 – Phytosanitary Treatments: methods to be followed for treatments of commodities and treatments of crops for containment or eradication of regulated pests.
EPPO Standards on plant protection products
- PP 1 – Efficacy Evaluation of Plant Protection Products: Standards on how to evaluate the efficacy of insecticides, acaricides, fungicides, herbicides, plant growth regulators and other products
. - PP 2 – Good Plant Protection Practice: Standards on optimal practice in protecting specific crops against their pests, including pathogens and weeds.
- PP 3 – Environmental Risk Assessment of Plant Protection Products: These Standards on the assessment of potential risks of environmental damage which may be caused by the use of plant protection products were withdrawn in 2018.
Standards approved by EPPO Council in 2025-09
At its last session (Paris, 2025-09-23/24), the EPPO Council approved the following draft standards. All of them are now in press and will be published in due course in the EPPO Bulletin. They will also be accessible from this website and stored in the EPPO Global Database.
EPPO Standards PM 1 - General Phytosanitary Measures
Additions to the A1 List (pests absent from the EPPO region)
- Xylotrechus pyrrhoderus (insect)
- Resseliella citrifrugis (insect)
Additions to the A2 List (pests locally present in the EPPO region)
- Ceratocystis ficicola (fungi)
- Euphorbia davidii (plant)
Transfer from the A1 to the A2 List
- ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma ulmi’ (phytoplasma)
- Ripersiella hibisci (insect)
EPPO Standards PM 3 - Phytosanitary procedures
-
PM 3/new General guidelines for the export certification process for plants, plant products or other regulated articles – NEW
-
PM 3/70 Compliance procedures for consignments of potato tubers at export and import (revision)
The following Standard has been WITHDRAWN:
- PM 3/29 General export inspection procedures for glasshouse and nursery
EPPO Standards PM 7 - Diagnostic protocols for regulated pests
- PM 7/122 Guidelines for the organization of interlaboratory comparisons by plant pest diagnostic laboratories (revision)
- PM 7/98 Specific requirements for laboratories preparing accreditation for a plant pest diagnostic activity (revision)
- PM 7/84 Basic requirements for quality management in plant pest diagnostic laboratories (revision)
The Council was informed that the following diagnostic protocols have been approved following the fast track procedure since the last Council meeting:
- PM 7/125 ELISA tests for viruses (revision)
- PM 7/011 Frankliniella occidentalis (revision)
- PM 7/160 Rhagoletis pomonella – NEW
- PM 7/026 Phytophthora cinnamomi (revision)
- PM 7/045 Cryphonectria parasitica (revision)
- PM 7/159 Stagonosporopsis chrysanthemi – NEW
- PM 7/158 Meloidogyne graminicola – NEW
EPPO Standards PM 9 - National regulatory control systems
-
PM 9/new Amaranthus palmeri and A. tuberculatus – NEW
EPPO Standards PP 1 - Efficacy Evaluation of Plant Protection Products
Specific Standards
- PP 1/002 Phytophthora infestans on potato and outdoor tomato (revision)
- PP 1/048 Migratory ectoparasitic and endoparasitic nematodes (revision)
- PP 1/085 Thrips on arable and vegetable crops in outdoor conditions (revision)
- PP 1/314 Evaluation of mating disruption techniques against lepidopteran pests in grapevine, pome and stone fruits under field conditions (revision)
- PP 1/144 Reduction of lodging in cereals and maize (revision)
- PP 1/new Spodoptera spp. in vegetables, strawberries and ornamentals – NEW
- PP 1/new Spodoptera frugiperda on maize – NEW
- PP 1/new Weevils in sugar beet - NEW
General Standards
- PP 1/242 Taint tests (revision)
- PP 1/243 Effects of PPP on biological transformation processes (revision)
- PP 1/296 Principles of efficacy evaluation for PPP based on low-risk substances (revision)
- PP 1/new Principles of effectiveness evaluation of PPP in a plant protection programme – NEW
- PP 1/new Assessing the adverse effects of PPP on russeting - NEW
EPPO approval procedure of Standards
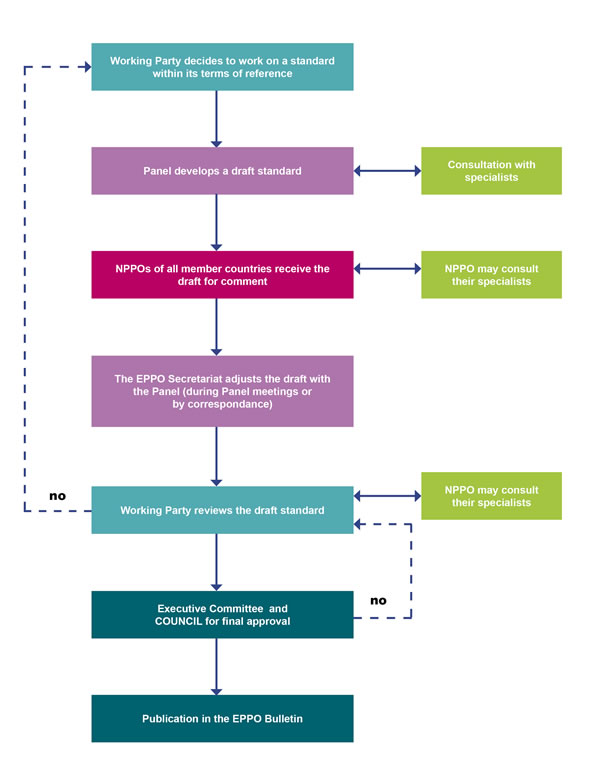
The flow diagram below summarizes the general approval procedure of EPPO Standards, but more detailed information can be found in a paper ‘Procedure for preparation and approval of EPPO Standards’ published in the EPPO Bulletin in 2019.